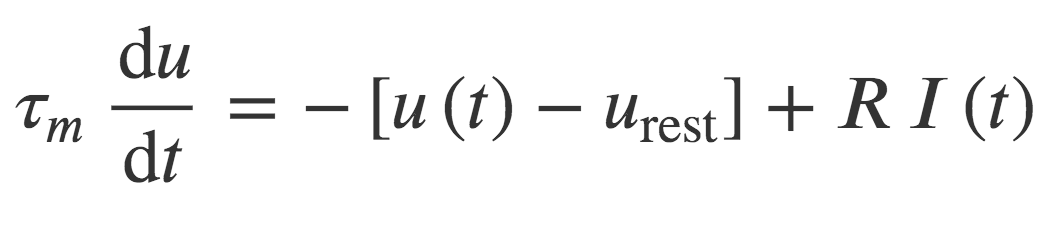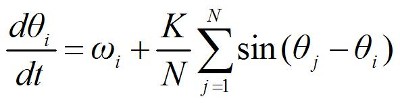from brian2 import *
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
# matplotlib.use("Agg")
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
# Define simulation parameters
neuronType = 'LIF' # 'Kuramoto', 'LIF'
BrianLogger.suppress_hierarchy('brian2.codegen') # suppress Brian warnings
useVariableDelays = True
groupLength = 20
N = groupLength**2
def getCentralLocation(groupLength):
firstRowLength = (groupLength-1)
columnsToCenter = groupLength * (int(groupLength/2)-1)
rowsToCenter = int(groupLength/2)+1
return firstRowLength + columnsToCenter + rowsToCenter
sourceNeuron = getCentralLocation(groupLength)
# -------------------------------------------
# Helper functions
# -------------------------------------------
# Define Gaussian function
def gaussian(distance, sig):
return np.exp(-np.power(distance, 2.) / (2 * np.power(sig, 2.)))
# Get Euclidean distance
def euclideanDistance(postSynapticLocation, preSynapticLocation):
return np.linalg.norm(postSynapticLocation - preSynapticLocation)
# Define function to get weight between two neurons
locations = [[x,y] for x in range(groupLength) for y in range(groupLength)]
@implementation('numpy', discard_units=True)
@check_units(i=1, j=1, sig=1, result=1)
def getDistance(i, j, sig=3):
preSynapticLocation = np.array(locations[int(i)])
postSynapticLocation = np.array(locations[int(j)])
distance = euclideanDistance(postSynapticLocation, preSynapticLocation)
return gaussian(distance, sig)
# Post-processing 1D to 2D data
def getRowIndices(groupLength):
rowStarts = [(i*groupLength) for i in range(groupLength)]
rowEnds = [((i+1)*groupLength) for i in range(groupLength)]
return rowStarts, rowEnds
def convertToMatrix(data, groupLength):
# Get row starts and ends
rowStarts, rowEnds = getRowIndices(groupLength)
# Initialise and then fill matrix
if len(data.shape)==1:
matrix = np.zeros(shape=[groupLength, groupLength])
for row in range(groupLength):
matrix[row,:] = data[range(rowStarts[row], rowEnds[row])]
elif len(data.shape)==2:
matrix = np.zeros(shape=[groupLength, groupLength, data.shape[-1]])
for row in range(groupLength):
matrix[row,:,:] = data[range(rowStarts[row], rowEnds[row]),]
return matrix
# -------------------------------------------
# Create network
# -------------------------------------------
print('Creating network...')
# Define LIF neurons and synapses
if neuronType == 'LIF':
tau = 10*ms
eqs = '''
du/dt = (-u + ISyn)/tau + (.1*xi*tau**-0.5) : 1
dISyn/dt = -ISyn * ms**-1 : 1
'''
G = NeuronGroup(N, eqs, threshold='u>1', reset='u=0', method='euler')
G.u = '.5*rand()'
trace = StateMonitor(G, ['u', 'ISyn'], record=True)
S = Synapses(G, G, on_pre='''ISyn += 4''', method='euler')
# Connect random input
randomInput = PoissonGroup(50, np.arange(50)*Hz + 25*Hz)
Sinput = Synapses(randomInput, G[sourceNeuron], on_pre = '''ISyn += .6''', method='euler')
Sinput.connect()
# Define Kuramoto neurons and synapses
if neuronType == 'Kuramoto':
eqs = '''
dTheta/dt = ((freq + (kN * PIF)) * ms**-1) : 1
PIF = .5 * (sin(ThetaPreInput - Theta)) : 1
ThetaPreInput : 1
freq : 1
kN : 1
'''
G = NeuronGroup(N, eqs, threshold='True', method='euler')
G.Theta = '1-(randn()*2)'
G.freq = '2*(i/N)'
trace = StateMonitor(G, ['Theta'], record=True)
S = Synapses(G, G, on_pre = '''ThetaPreInput_post = Theta_pre''', method='euler')
# Connect synapses with distance-dependent connectivity
S.connect(condition='i!=j', p='getDistance(i,j)')
# Define synapse delays
if useVariableDelays==True:
delayGaussianSigma = 3
for syn in range(len(S)):
currentI, currentJ = S.i[syn], S.j[syn]
S.delay[syn] = 1/getDistance(currentI, currentJ, delayGaussianSigma) * ms
# 1/getDistance(currentI, currentJ, delayGaussianSigma) * ms
# euclideanDistance(currentI, currentJ) / 3.5*ms
# Run simulation
print('Running simulation...')
duration = 10*ms
if neuronType == 'Kuramoto':
G.kN = 3
run(duration, report='text')
G.kN = 0
run(duration*6, report='text')
G.kN = 3
run(duration, report='text')
G.kN = 0
run(duration*6, report='text')
if neuronType == 'LIF':
run(duration*10, report='text')
# -------------------------------------------
# Plot results
# -------------------------------------------
# Animation
fig = figure(2, figsize=(6,6))
fig.set_facecolor((.8,.8,.8))
gca().set_facecolor((.8,.8,.8))
# Set up formatting for the movie files
Writer = animation.writers['ffmpeg']
writer = Writer(fps=15, metadata=dict(artist='Me'), bitrate=1800)
# Get trace of interest
if neuronType == 'LIF':
traceOfInterest = trace.u
elif neuronType == 'Kuramoto':
traceOfInterest = (cos(trace.Theta)+1)/2
axis('off')
# Initialise figure
def updatefig(t):
global thetaMatrix
im.set_array(np.transpose(thetaMatrix[:,:,t]))
if t > 10:
fig.set_facecolor((0,0,0))
return im,
thetaMatrix = convertToMatrix(traceOfInterest, groupLength)
im = imshow(thetaMatrix[:,:,0], animated=True)
im.set_cmap('bone')
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, updatefig, frames=traceOfInterest.shape[1], interval=1, blit=True)
# ani.save('travellingWaves_%s.mp4' % (neuronType), writer=writer)
show()